angularjs 1.4.5의 분석 정보
angularjs 1.4.5의 분석
본문
1. 브라우저가 Angular.js 파일을 읽고 실행한다.
2. DOM Content Loaded Event 트리거를 기다린다.
// check if document is already loaded
if (document.readyState === 'complete') {
setTimeout(trigger);
} else {
this.on('DOMContentLoaded', trigger); // works for modern browsers and IE9
// we can not use jqLite since we are not done loading and jQuery could be loaded later.
// jshint -W064
JQLite(window).on('load', trigger); // fallback to window.onload for others
// jshint +W064
}
3. 트리거가 오면 Angularinit을 실행한다.
jqLite(document).ready(function() {
angularInit(document, bootstrap);
});
4. anuglarinit에서 HTML구조를 파싱해서 ng-app을 찾는 것 같습니다. ng-, data-ng-, ng:, x-ng- 네개의 프리픽스를 찾아보네요.
var ngAttrPrefixes = ['ng-', 'data-ng-', 'ng:', 'x-ng-'];
------
function angularInit(element, bootstrap) {
var appElement,
module,
config = {};
// The element `element` has priority over any other element
forEach(ngAttrPrefixes, function(prefix) {
var name = prefix + 'app';
if (!appElement && element.hasAttribute && element.hasAttribute(name)) {
appElement = element;
module = element.getAttribute(name);
}
});
forEach(ngAttrPrefixes, function(prefix) {
var name = prefix + 'app';
var candidate;
if (!appElement && (candidate = element.querySelector('[' + name.replace(':', '\\:') + ']'))) {
appElement = candidate;
module = candidate.getAttribute(name);
}
});
if (appElement) {
config.strictDi = getNgAttribute(appElement, "strict-di") !== null;
bootstrap(appElement, module ? [module] : [], config);
}
}
5. 위에서 html에 ng-app가 있으면 appElement = 'html'이 되고, body에 있으면 body를 가지고 bootstrap으로 넘어 가네요
Automatic Initialization
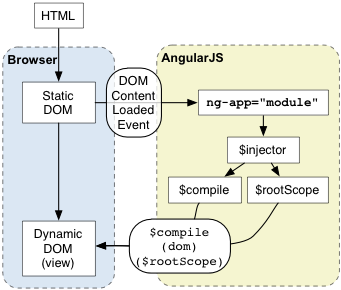
Angular initializes automatically upon DOMContentLoaded event or when theangular.js script is evaluated if at that time document.readyState is set to'complete'. At this point Angular looks for the ng-app directive which designates your application root. If the ng-app directive is found then Angular will:
- load the module associated with the directive.
- create the application injector
- compile the DOM treating the
ng-appdirective as the root of the compilation. This allows you to tell it to treat only a portion of the DOM as an Angular application.
<!doctype html>
<html ng-app="optionalModuleName">
<body>
I can add: {{ 1+2 }}.
<script src="angular.js"></script>
</body>
</html>As a best practice, consider adding an ng-strict-di directive on the same element as ng-app:
<!doctype html>
<html ng-app="optionalModuleName" ng-strict-di>
<body>
I can add: {{ 1+2 }}.
<script src="angular.js"></script>
</body>
</html>This will ensure that all services in your application are properly annotated. See the dependency injection strict mode docs for more.
0
댓글 2개

저 고민되요.

